We use RFID for various purposes like attendance, Fleet management, Tracking and so on. As these tags are at the user ends they can bring greater vulnerability to the organization access level.
Contents
- Introduction
- RFID Is Not RF
- Recent Attacks In RFID
- Security Requirements
- Common Attack surfaces
- Cryptographic Implementations
- Conclusion
Introduction
RFID is a device which works basically on the electromagnetic waves. Its operating frequency varies from 135KHz - 5.8GHZ and these are closely coupled circuits. It is similar to the smart card. The transponder is composed of either inductive or capacitive radio coupling. There are two main components of RFID. They are,
- Transponder- an object to be identified.
- Reader (or) Interrogator-which is used to communicate with the transponder.
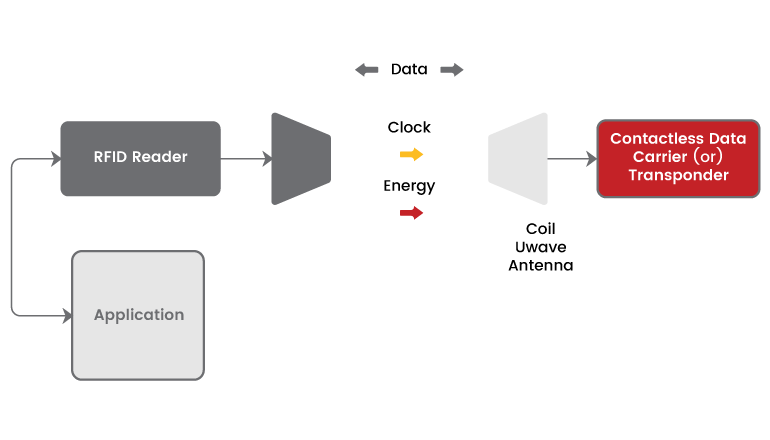
RFID is not RF
Both RFID and RF works on the same electromagnetic waves. The main difference between these two RFID is just used to intimate the reader that the transponder is here and by using RF we can perform multiple operations but one at a time. As stated above both operate at different frequency range following FCC standards. RFID falls under (NFC) near field communication category while the RF can be used to transmit over a long distance by use of amplifiers and repeaters.
Recent Attacks In RFID
Attacks on RFID usually take place due to improper installation and lack of authorization. The recent attack took place in the CRC part of the machine. The verification part consists of a simple XOR gate formula which the intruders used this flaw in the CRC to bypass the reader where they found the 32 bits data transmitted for every 4ms and form the extracted data he flashed an new card and with no time the machine accessed.
Security Requirements
The device security can be distinguished into two categories based on the area of usage, such as,
- Industrial or closed application
- Public applications
You may get confused of how the device is been classified, so based on the application let us thrive into an example, consider a ramp which is in motion where each product in the ramp has its own RFID tag. For the purpose of tracking here transponders are always kept active which turns the device ready for spoofing and jamming and also leads to wastage of power. In public ticketing system individual user has a physical access and we cannot identify the intruder as it is in place in public, whereas in the case of the industry it is only possible for the employer to act as an intruder. So now let us dig deeper into the attacks as they can be classified into two major categories.
- Common attack surfaces
- Cryptography implementations
Common attack surfaces
These attacks are performed by the intruder with adequate knowledge and to do this it is not necessary for him to know about the entire architecture or the systems working process. The various categories of the common attack surfaces are listed below,
- Attacks on Transponders
- Spoofing & cloning of transponders
- Attacks on RF interface
- Eavesdrop
- Jamming
- DOS
Attacks on Transponders
The transponders simply resembles as a credit/debit card which is used to provide access to the user to step in/out of the premise. The attack on transponder gets varied based on the type of transponder used. For example consider an attack in which the intruder tries to perform a permanent destruction of the transponder. This attack can be performed by exposing the antenna in a strong field, in which the maximum field of an antenna should be greater than 12A/m for a frequency of 13.56MHz for inductive coupled transponders. In this case the transponder is introduced in a strong electromagnetic field thereby producing an extreme heat which turns the transponder to destroy thermally else if the intruder cannot introduce in strong electromagnetic field then he can use the microwave to induct it.

Transponder shielding/Tuning
This attack does not require the intruder to be skilled an intruder with no skills can perform this task this is simple, just like wrapping up a thing. Here the intruder should have the transponder in hand and he requires a metal surrounding it, whereas in this case we can use an aluminum foil surrounding the transponder which produces an UHF scatter thereby resulting in an eddy current loss which makes insufficient for the reader to detect the transponder.
Spoofing & cloning of Transponder
To start with this attack we should initially determine the type of transponder, either it is a read-only or read-write one. As this might affect the intruder attacking scenarios.
Read-Only Transponders
These attacks are carried out in contact-less RFID interface (i.e)., when a transponder reaches the sufficient distance to the reader it automatically detects the transponder and it logs the data where the transponder's acknowledgement should be sent. Then the reader will send a data frame to enhance the operation where this signal contains all useful information about the transponder, then number the user name with some manufacturer constraint details. By the use of certain interceptor the intruder can intercept the signal and that can be useful for them to construct a cloned copy of the transponder by which the intruder can perform unauthorized access.
Transponders with writable memories
Transponders with writable memory can be simply read by the intruder without any basic knowledge but they should know the usage of the tool. By using a perfect RFID reader/writer the intruder will not only perform cloned copy of cards but he can also overwrite the existing memory of the card. This can be efficiently prevented by the use of perfect encryption in areas of communications and needs to apply proper A&A mechanism wherever possible.

Attacks on RF interface
RFID works on electromagnetic waves either in near field or in far-field. To capture the RF interface the intruder does not require a physical access instead he needs to be skilled in the area of communication and to understand and work with the signal characteristics. The various attacks in the RF interfaces are,
- Communication interception between the transmitter and the receiver (Eavesdrop).
- Communication interception between the transmitter and the receiver (Jamming).
- Extending the read range in order to skim the transponder
- Blocking the reader with DOS attack.
- Undetected use of remote transponder through a relay attack.
For further details/queries just drop an mail to [email protected]
Eavesdrop
The intruder needs a suitable antenna tuned at 13.56MHz to intercept a medium frequency at a distance of 3m. Successful attack requires less bandwidth but whereas in the real time we will receive more bandwidth of signal which takes more time for the analyst to come into conclusion by taking the average of the signal.
Jamming
This technique is an entirely different form, as this would not provide any useful information for the attacker instead the intruder can hold/delay the operation for neither a while nor the intruder feels to enjoy it. This can be done with minimum skills with specific hardware in the hands of an intruder. RFID jamming is overwhelmed.
DOS
RFID communicates with large no of transponders using serial communication contactless method (i.e)., it communicates with the transponder via a slotted ALOHA neither uses a BST(Binary Search Tree) where it TX/RX are as binary values as 1 and 0. By the use of the blocker tag, we can take down the system in which the BST would take 2^k values where k is the no of bits in serial number. If a reader needs to crack an password it would be calculated as follows tg=t1*2n where n is the no of bits. For an individual serial number for running the entire series it would tale about approximately 8000 days which is obsolete. Hence to perform this action we need a full blocker or universal blocker. Even the widely used slotted aloha can be blocked by using a blocker tag.
Tools
- Proxmark
This hardware can provide end-end security for an organization/supply chain users. As these tools are expensive and they are found in the hands of penetration testers, RFID enthusiast, Security researches. By using this one can able to build robust RFID machines resistances free from cyberattacks.
Cryptography Implementations
Attacks on RFID takes place more on the part of CRC and parity checks. Strong cryptography implementation in each level of RFID makes the attacker fatigue thereby securing your device from cyberattacks.
Authentication using derived keys
This is one of the most traditional methods used by the manufactures to reduce the manufacturing cost of the device thereby sharing a common key between all the transponders and the readers. For example, consider a metro station where the public used to get ticket by recharging the given transponders; in this the transponders will communicate with the reader whenever it reaches a certain distance; if all the transponders use a common key shared between them then it will be easy to capture the RF interface within a certain distance. So, to eliminate this problem the manufacturer should use a unique id for each of the transponders which contain a read-only category.
Encrypted Data Transfer
Traditional methods involves the use of same keys which can be sniffed by using certain RF algorithms. In modern era researchers are trying to incorporate a unique MAC address to each and every transponders. Moving further, they also applied the usage of WEP keys, DES keys and AES algorithms to add more security to the device. Let us just have a look at the below image.
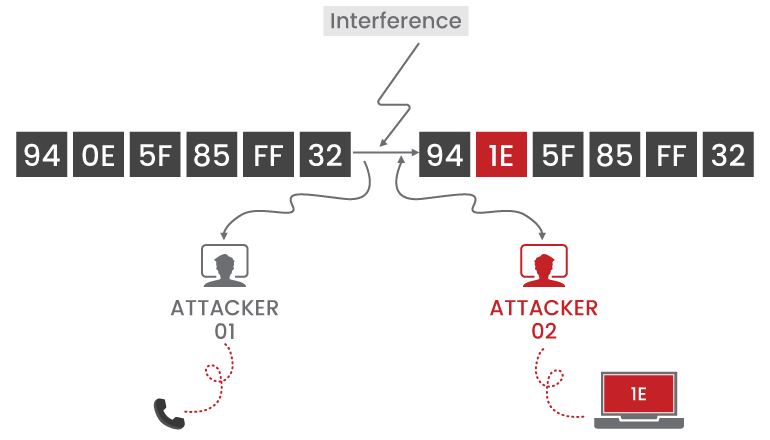
This above image represents a process of data transfer from the transmitter. In this use case let us consider that we have two attack scenarios, one is passive scanning algorithm and the other is used to alter the captured data frames for the fruitful attack.
Let us assume that the key should be shared between the TX and the RX for decryption. In this the key would also be transmitted in the air so it is possible for the intruder to capture that too. A single miscalculation may lead to system take over.
In order to avoid this we need to transmit the data on a hex code format in which this encryption should be done before we start transmitting and at the receiver end the decryption frame format is specified within the receiver. The main concept is that the produced key should be changed dynamically for each and every transfer of signal from the transmitter. Dynamic key can be generated by the use of stream cipher. This is one of the efficient ways to avoid the Encrypted data transfer. Luckily these are followed by only few vendors.
Conclusion
RFID can operate at three different ranges namely LF, HF and UHF in most of the cases we use HF transponders for our public ticketing and login premises at our office and the UHF are used in toll plazas. For each category of RFID there are low cost cloning and RFID writers are available in Chinese websites. There are various vendors available; hence it is responsible for the user to opt it. Briskinfosec recommends before choosing the RFID it is better to look at the international standards like ISO,IEC and when you opt for cheaper things make sure that it is using strong cartographic algorithms to avoid security breaches.
Resources
You may be also interested on
- Layer wise security of analysis in IoT
- Dumpster diving- Your unused hardware/modem can leak your critical data
- Why you might be failing at the hardware attack






