Introduction
The primary goal was to create an ontology that would serve as a common language for developers, architects, operators, business owners, security engineers, purchasers, and suppliers/vendors, allowing for straightforward communication and assisting in the resolution of difficulties. Symptoms, mitigations, and controls in this problem area are also identified by the study.
Automated bots are the favoured method for online scraping, evading CAPTCHA obstacles, and engaging in malicious actions such as spamming, account takeover, credential stuffing, sniping, and carding. The criminals behind these deceptive schemes are constantly developing automated programmes to create increasingly more advanced persistent bots that can accurately mimic human behaviour to avoid discovery.
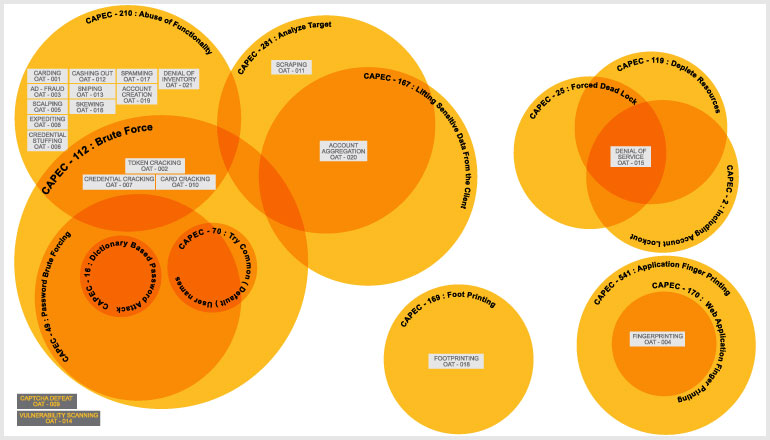
The surge of automated bot attacks on web applications has prompted the Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP), an online community dedicated to enhancing software security, to take action. OWASP launched the first Automated Threat Handbook in late 2015 to help organisations better understand and respond to the significant worldwide increase in automated threats from bots, to stay up to current on the latest online security concerns. Account Credentials, Payment Cardholder Data, Vulnerability Identification, and Other Automated Risks are the four primary categories that the manual divides the Top 20 automated threats into.
Account Credentials
- OAT-020 Account Aggregation
- OAT-019 Account Creation
- OAT-007 Credential Cracking
- OAT-008 Credential Stuffing
Payment Cardholder Data
Vulnerability Identification
- OAT-018 Footprinting
- OAT-014 Vulnerability Scanning
- OAT-004 Fingerprinting
Other Automated Threats
- OAT-003 Ad Fraud
- OAT-009 CAPTCHA Defeat
- OAT-015 Denial of Service
- OAT-006 Expediting
- OAT-005 Scalping
- OAT-011 Scraping
- OAT-016 Skewing
- OAT-013 Sniping
- OAT-017 Spamming
- OAT-002 Token Cracking
- OAT-021 Denial of Inventory
Account Credential
Today's advanced bots may acquire enough user credentials to cause a serious web security breach, with financial losses and stolen data, as well as scams and identity theft, as a result. It is sub-divided into four different categories:
OAT-020 Account Aggregation
Multiple account credentials and other information are gathered into a single system through Account Aggregation. An application like this can be used to aggregate account information from different apps or data from multiple accounts in a single app. Suspicious account information access behaviour patterns (e.g., geolocation, time zones) that do not match the user profile or a lack of end-user engagement with the service provider are some of the most obvious symptoms of account aggregation activities.
OAT-019 Account Creation
Account Creation allows a user to sign up for many accounts on an app by using the app's account sign-up methods. This dangerous event has the potential to boost a website's reputation artificially, skew SEO, and generate mass content spam. A higher-than-average account creation rate compared to the average rate over time, or accounts with inadequate information compared to typical account holders, are two of the most prominent indications of account creation.
OAT-007 Credential Cracking
By attempting different usernames and passwords, automated programmes or bots can identify genuine login credentials. A surge in the number of failed login attempts and account lock rate, as well as a large number of web requests including variations on the account name and password, are all symptoms of credential cracking activity.
OAT-008 Credential Stuffing
Credential stuffing is a threat in which stolen authentication credentials from one application are used against another to verify if the victim has reused the same login credentials. Credential stuffing can manifest itself in a variety of ways, including several login attempts with different credentials from the same HTTP client or a large number of failed login attempts.
Payment Cardholder Datas
When bad bots can extract account credential information, it becomes significantly easier for bad bots' operators to steal payment cardholder information. It's broken down into four sub-categories:
OAT-001 Carding
Carding is a technique for identifying useful data and weeding out invalid credit card/debit card information. Carding is the process of comparing a group of complete sets of cardholder information to the payment process of a merchant. A rise in basket desertion, a decrease in average basket price, a higher proportion of failed payment authorizations, excessive use of the payment step, or an increase in chargebacks are some of the most visible symptoms of carding activity.
OAT-010 Card Cracking
By attempting various values, automated assaults are used to find missing start/expiry dates and security codes for stolen credit card data. A spike in basket abandonment, a large proportion of rejected payment authorizations, disproportionate use of the payment step, a fall in average basket pricing, or an increase in chargebacks is some of the most prevalent signs of card cracking danger.
OAT-012 Cashing Out
Bots can be designed to purchase items or cash using stolen payment cards or other user account data that has been validated. If a well-deployed bad bot setup targets a web application, it may theoretically collect cardholder details, steal money, and resell personal account information before you even notice or react. An increase in chargebacks, an increase in the use of interconnected accounts (e.g., same phone number, same password, identical or similar email address), an increase in demand for higher-value goods or services, or an increase in demand for a single supplier's products or services are some of the most obvious signs of cashing out an activity.
Vulnerability Identifications
According to the Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP), there are hundreds of flaws that could compromise a web application's security, and it only takes the detection of one to give a hacker access to sensitive consumer or corporate data. The discovery of possible targets lends itself well to automation and automated attacks. The following are the categories:
OAT-018 Footprinting
Footprinting is the process of exploring an application for vulnerabilities and identifying all of its URL pathways, parameters and values, and process sequences to determine its attack surface area. Increased system and application error codes, such as HTTP status codes 404 and 503, in the same user session, or users who exercise the entire application's capability in a way that differs from ordinary user behaviour, are some of the most common indicators of footprinting activity.
OAT-014 Vulnerability Scanning
Vulnerability Scanning searches and fuzzes apps, looking for web security vulnerabilities in all available content locations, paths, file names, and parameters. A high occurrence of errors (e.g., HTTP status code 404 not found, data validation and authorization failures), extremely high application usage from a single IP address, a high ratio of GET/POST to HEAD requests for a user session compared to typical users, or multiple misuse attempts against application entry points are some of the most obvious signs of vulnerability scanning.
OAT-004 Fingerprinting
Fingerprinting sends queries to an application to collect data and create a profile of the application's supporting software and framework types and versions. The probe scans for HTTP header names and values, as well as session identifier names and formats, to identify application components. Single HTTP requests (just one request from that browser/session/device/fingerprint) or requests for resources that are rarely requested are some of the most prominent signs of fingerprinting activity.
Other Automated Threat
OAT-003 Ad Fraud
Ad fraud is the intentional manipulation of the number of times an item, such as advertising, is clicked on or displayed. The goal of ad fraud is usually to increase the number of clicks. Some of the most evident signs of ad fraud can be low conversion ratios during spikes, unusual peaks in the number of clicks or impressions or high bounce rates during peaks in impressions or clicks.
OAT-009 CAPTCHA Defeat
CAPTCHA fraud uses automation to find the correct response to such tests (including visual, auditory, and puzzle). CAPTCHA Bypass by bots can manifest itself as a high CAPTCHA solving success rate on fraudulent accounts, as well as suspiciously rapid or fixed CAPTCHA solving timeframes.
OAT-015 Denial of Service
Bots that simulate legitimate users are used in denial-of-service attacks to drain an application's resources, such as its file system, memory, processes, threads, CPU, and human or financial resources. Spikes in CPU, memory, and network use, unavailability of part or all of the application, an increase in user account lockouts, or reduced weblog traffic are some of the most obvious indications of denial of service.
OAT-006 Expediting
Expediting is an automated threat that exploits speed to manipulate an application for personal gain, allowing perpetrators to move through a succession of application processes quickly. High-frequency trading and algorithmic trading in financial contexts, as well as gold farming in games, are examples of expediting. Unusually quick progress through multi-stage procedures is one of the most typical indicators of Expediting activity.
OAT-005 Scalping
Scalping is a method of obtaining limited-availability and scarce commodities in large quantities while denying other users access to them. It's commonly used to buy tickets and resale them at a profit. High peaks in demand for specific limited-availability items or services, or a surge in the circulation of limited commodities reselling on the secondary market, are some of the most obvious symptoms of scalping.
OAT-011 Scraping
Scraping is done on a large scale using automated computer scripts that download original content and upload the same on new platforms. Scrapers can use compromised or fake accounts or collect data from accessible paths and parameters. Some of the most common symptoms of scraping can be unusual request activity for selected resources.
OAT-016 Skewing
Skewing is the process of automating clicks and requests to intentionally inflate or skew a given application measure. It can also be used to increase the number of visitors to a website. Reduced click/impression to result in the ratio (e.g., check out, conversion), unexpected or unexplained changes to a measure or metrics that differ considerably from industry norms are some of the most obvious symptoms of skewing.
OAT-013 Sniping
Sniping is an automated threat that lets users act at the last possible moment, preventing genuine users from responding in kind. Auctions are the most well-known example of sniping. Sniping can manifest itself in several ways, including an increase in user complaints about being unable to receive goods/services or some users having a higher success rate than expected.
OAT-017 Spamming
Spamming, for example, dilutes comment threads with questionable content, boosts SEO, or disseminates malware by sending malicious or other types of incorrect information to databases and user communications. An increase in the rejection rate of user-generated content by moderation systems, as well as a high percentage of user complaints regarding spam content, are some of the most obvious symptoms of spamming.
OAT-002 Token Cracking
Token cracking is a method of obtaining cash, credit, or discounts by identifying token codes such as coupon numbers and voucher codes, sometimes by brute force. Multiple failed token attempts from the same user, IP address, user agent, device ID/fingerprint, or a high frequency of failed token attempts are some of the most prevalent signs of token cracking activity.
OAT-021 Denial of Inventory
Automated bots are used to choose and hold products from a restricted inventory or stock, but they are never actually purchased, paid for, or confirmed, preventing other users from doing so. A rapid decrease in inventory balance, an increase in product retained in baskets or reservations, or increased basket abandonment are all symptoms of inventory fatigue.
Conclusion
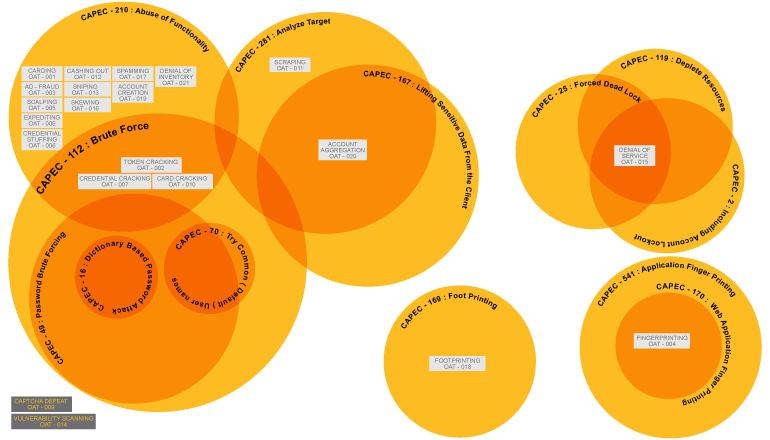
We have just discussed the automated attacks used by the attackers to target the organization/ individual. Implementing a few preventive measures and educating the employees might slow down the process of the attack. By following this Owasp Model, the Misuse of inherent functionality, business logic flaws and related design flaws can be identified.