Table of Contents
As you all know, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is not only responsible for regulating the Indian banking system and currency but also for reducing financial crimes such as money laundering and terrorism financing. To address these risks, the RBI has established cybersecurity guidelines that financial institutions, including banks like commercial banks, must follow. Institutions that comply with these frameworks are considered RBI compliant. We should be aware of the RBI's Cybersecurity Framework. For better understanding, I have summarized them in a shorter format to help you easily grasp the core concepts.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has established circulars that outline cybersecurity guidelines to protect financial institutions from cyber threats. These guidelines set security standards for banks and payment system operators, ensuring risk mitigation and data protection.
Key RBI Cybersecurity Guidelines along with the circular:
RBI Cyber Security Framework for Banks & UCBs
Evaluates cybersecurity practices in banks and UCBs to counter cyber threats and fraud, referencing RBI Circular No. DBS.CO/CSITE/BC.11/33.01.001/2015-16 for ensuring system security and resilience.
Aligning RBI Guidelines with the Three-Tier Security Framework
The RBI cybersecurity guidelines support a structured, three-tier security approach, ensuring institutions like banks implement security controls based on risk levels. The 1st Tier focuses on Baseline Security Requirements, which form the foundation of an institution's cybersecurity posture. Failure to implement these baseline measures can weaken overall security, making systems vulnerable to threats.
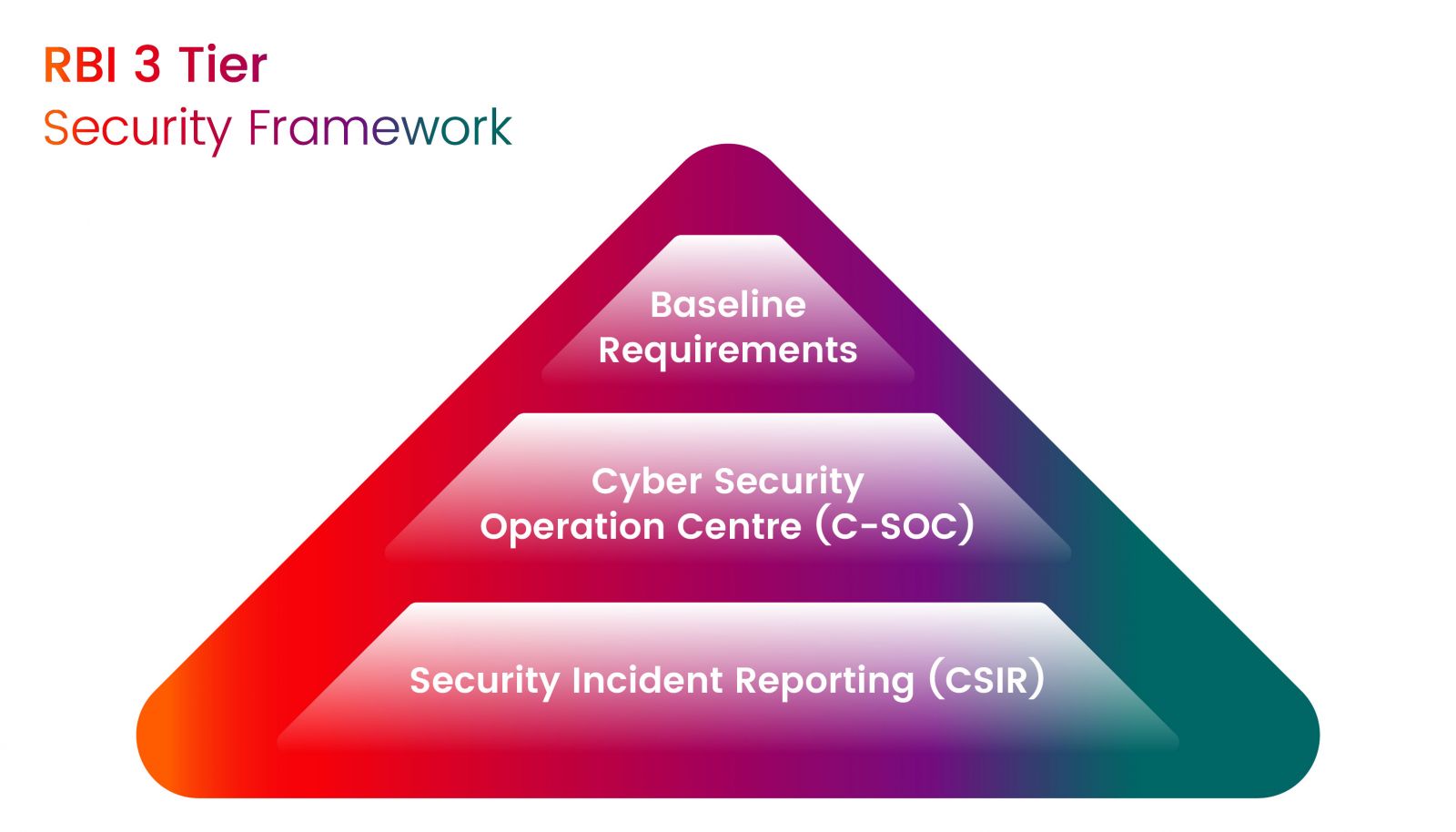
The top tier, or the 1st tier, is the baseline requirements
-
Data Leak Prevention Strategy: Developing plans to prevent both intentional and unintentional leakage of sensitive data, often through the use of Data Loss Prevention (DLP) tools.?
-
User Access Control: Implementing role-based access controls to ensure employees have appropriate access to confidential data, thereby preventing misuse.?
-
Patch Management: Ensuring timely application of patches to systems and devices to address known vulnerabilities.?
-
User Training and Awareness: Regularly training employees on handling sensitive data securely, including best practices for sharing and processing information.?
-
IT Asset Inventory: Maintaining a comprehensive inventory of all IT assets to ensure visibility and effective risk management.?
-
Vendor Risk Management: Establishing processes to assess and manage risks associated with third-party vendors, ensuring they comply with the bank's security standards.?
The middle tier is the Cyber Security Operation Centre (C-SOC)
This section mandates the establishment of a Cyber Security Operation Centre to provide continuous monitoring of the bank's environment. It emerges the need for appropriate tools, clearly defined policies and procedures, and technically competent security staff to monitor all the activities happening to mitigate incident occurring
The last tier is the Security Incident Reporting (CSIR)
This section details the requirements for reporting security incidents, ensuring that banks have mechanisms in place for timely detection, response, recovery, and containment of cyber incidents to prevent them from spreading and exposing sensitive information
We have covered the cybersecurity aspect, and now the most important section is what happens if banks fail to comply with the RBI cybersecurity framework.
Consequences of Non-Compliance Faced by Banks
RBI imposed a penalty of 3.95 crores on Kotak Mahindra Bank
In April 2024, Kotak Mahindra Bank was penalized 3.95 crore by the RBI due to IT security lapses and operational resilience deficiencies. The bank failed to implement robust cybersecurity measures, which exposed it to potential data breaches and security risks. After the penalty, Kotak Mahindra Bank addressed the identified gaps, and an external audit conducted by the RBI later verified their compliance with the RBI’s Cybersecurity Framework.
Punjab National Bank (PNB) Penalized 2 Crore for Security Lapses
Punjab National Bank faced a 2-crore penalty in January 2024 for failing to address vulnerabilities identified in its internet banking platform. The security flaws included:
-
Outdated firewall configurations that failed to block suspicious traffic.
-
Absence of endpoint monitoring tools to detect malicious activities.
-
Delayed response to critical security patches that exposed customer data to potential threats.
Yes Bank Penalized 1.5 Crore for Non-Compliance
Yes Bank was fined 1.5 crore in February 2024 for failing to implement adequate security controls as mandated by the RBI. The gaps identified included:
-
Inadequate identity and access management controls allow unauthorized access to customer data.
-
Failure to maintain proper audit trails, resulting in undetected suspicious activities
-
Insufficient data backup strategies increase the risk of data loss in a cyberattack.
These incidents highlight the importance of conducting regular security assessments and addressing potential gaps on a defined schedule. With proper consultancy guidance and proactive measures, these risks can be mitigated effectively.
Remediation and Compliance Measures
To achieve compliance with RBI's cybersecurity framework, financial institutions should implement the following strategies:
Not only are there penalties for non-compliance with cybersecurity guidelines, but financial institutions can also face fines for failing to meet general regulatory requirements for example like Under-reporting/Misreporting of Income, Failure to Maintain Books of Accounts and Other Documents etc. However, penalties for cybersecurity non-compliance tend to be higher. This is because cybersecurity lapses can lead to significant operational, reputational, and financial damage. To address these risks, RBI has implemented stricter penalties for security-related violations to ensure stronger protection for the financial data.
Now, it is essential to explore the remediation measures and action plans that financial institutions can adopt to achieve compliance with RBI's cybersecurity regulations and set an example for others in the industry.
Best Practices for RBI Compliance Easy Checklist
To ensure compliance with RBI's cybersecurity regulations, financial institutions should follow these best practices:
1. Strengthening Cyber Governance
-
Appoint a Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) with board-level reporting.
-
Conduct annual cybersecurity risk assessments.
-
Implement a Cybersecurity Governance Framework aligned with RBI guidelines.
2. Enhancing Threat Detection & Incident Response
-
Deploy SIEM (Security Information & Event Management) systems for real-time monitoring.
-
Establish an Incident Response Team (IRT) with defined escalation procedures.
-
Conduct regular incident response simulations and tabletop exercises.
3. Regular Security Testing & Audits
-
Perform quarterly VAPT (Vulnerability Assessment & Penetration Testing).
-
Conduct audits of IT and OT environments regularly.
-
Ensure data encryption and secure backup strategies.
4. Strengthening Third-Party & Vendor Security
-
Implement Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) policies.
-
Assess vendor security and compliance regularly.
-
Enforce cybersecurity compliance obligations in vendor contracts.
5. Employee Awareness & Phishing Prevention
-
Conduct regular cybersecurity awareness training for employees.
-
Run simulated phishing campaigns to prepare employees for potential threats.
- Enforce strict access controls and multi-factor authentication (MFA)
At Briskinfosec, we provide detailed solutions designed to help financial institutions meet RBI's cybersecurity requirements effectively. Our approach includes
-
Conducting Gap Assessments – Identifying security gaps in your current infrastructure and recommending appropriate steps to address them, ensuring alignment with RBI's cybersecurity framework .
-
Performing VAPT (Vulnerability Assessment & Penetration Testing) – Evaluating systems, networks, and applications for vulnerabilities to enhance security resilience.
-
Suggesting Security Controls – Providing better technical security controls and solutions to strengthen your institution's cybersecurity posture.
-
Providing Cybersecurity Training – Educating employees, particularly those involved in banks' daily operations, to identify and respond to phishing attacks effectively.
-
Conducting Phishing Simulation Campaigns – Running real-world phishing attack simulations to test employee awareness and boost confidence in handling cyber threats.
-
Assisting in Incident Response Planning – Helping organizations develop robust incident response strategies to detect, respond, and recover from cyber incidents efficiently.
-
Ensuring Regulatory Compliance – Aligning cybersecurity practices with RBI's guidelines, preventing non-compliance risks, and ensuring a secure banking ecosystem.
We are committed to guiding and assisting you in becoming a role model for other financial institutions by implementing strong cybersecurity practices, ensuring regulatory compliance, and promoting a security-first culture within your organization.


