Contents:
- Introduction to DMARC
- DMARC Working Process
- DMARC Record Breakdown
- Aggregate DMARC Report
- Why DMARC is Necessary
- DMARC Misconfiguration Threat
- Conclusion
Introduction to DMARC:
DMARC also known as Domain Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance is a technical standard that helps protect email senders and recipients from email related spoofing and phishing attacks which are widely used as a part of social engineering techniques to compromise user’s systems. It uses SPF (Sender policy framework) and DKIM (Domain Keys Identified Mail) to validate the authenticity of a mail.
DMARC record policy can be published by an organization to define their mail authentication practice and provides instructions to receiving mail servers on how to enforce them.
Specifically, DMARC establishes a method for a domain owner to:
- Publish its email authentication practices
- State what actions should be taken on mail that fails authentication checks
- Enable reporting of these actions taken on mail which looks to be from its domain.
DMARC Work Process:
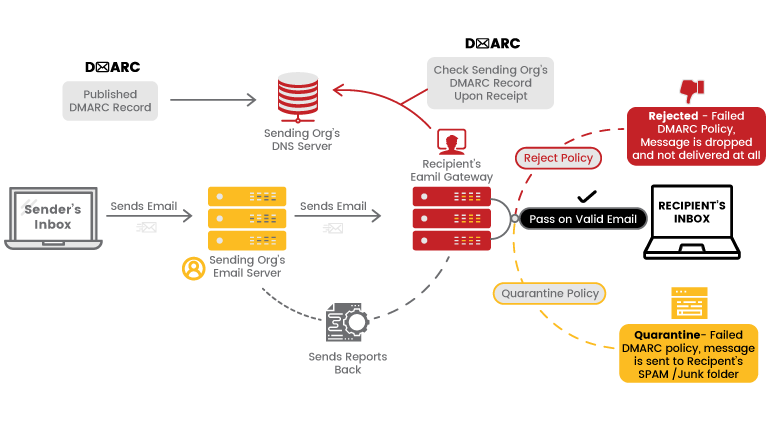
As explained above, DMARC uses SPF and DKIM for email authentication. In general terms, the process of DMARC validation works like this:
- A domain administrator publishes DMARC Policy which defines its email authentication procedure and how receiving mail server should handle the mails which violate the policy.
- When a mail server receives an email, it uses DNS to look up the DMARC policy of the sender domain contained in the From address. The receiving server then check for
1. Does the message’s DKIM signature valid?
2. Did the message come from IP addresses allowed by the sending domain’s SPF records?
3. Do the headers in the message show proper “domain alignment”?
- Using the above information, the receiving mail server can apply the DMARC policy of sending mail server to decide whether the mail is legit or not.
- Once done with the above step, the receiving mail server will send a report mail to the sending domain owner.
DMARC Record Breakdown:
DMARC record is stored in a domains’ DNS databases i.e, it is possible to view the DMARC record of a domain using DNS query tools like dig, host dnsenum etc., or some online DNS lookup sites. We have used the dig tool in kali Linux to perform a DNS lookup of the DMARC record for a domain.
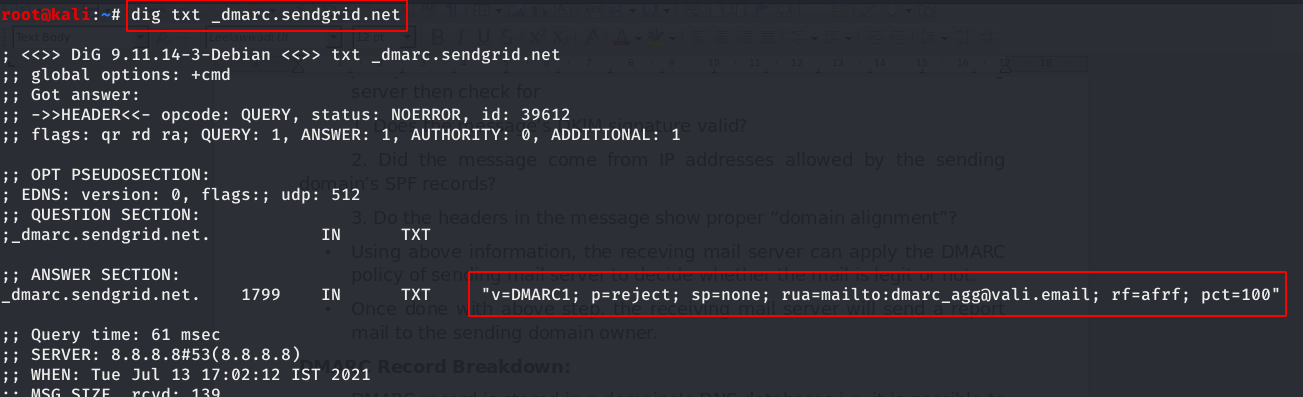
As we can see from above screenshot, the DMARC record looks like below
v=DMARC1;p=reject;rua=mailto:[email protected];ruf=mailto:[email protected];rf=afrf;pct=100
Lets breakdown each section of the DMARC record,
“v=DMARC1” specifies the version of the DMARC protocol used.
“p=none” This specifies the DMARC policy of sending domain is set to none.
Apart from this, the policy can have different values like reject and quarantine.
Policy value none tells the receiving server to not take any actions when the mail is not authenticated properly. Also, it will force the receiving server to send a mail report to sending domain admin’s mail id which is present in rua=mailto value.
Policy value of reject tells the receiving server to completely deny the mail if it's not validated 100% by sending domain.
The policy value of quarantine tells the receiving server to quarantine the mail if not validated ie send the mail to the spam folder.
“rua=mailto:[email protected]” This part insists the receiving server send DMARC aggregate reports to the mentioned mail id of sending domain owner.
“ruf=mailto:[email protected]” This part insists the receiving server send DMARC forensic reports to the mentioned mail id of sending domain owner.
“rf=afrf” refers to the reporting format.
“pct=100” Percent – This part tells the receiving server how much of their mail should be subjected to the DMARC policy’s specifications.
Besides the above-mentioned configurations in the DMARC record, there are other configurations available for the DMARC record which can be configured by the Domain administrator. They include sp (policy for subdomains), RI (time interval between aggregate reports) and adkim (DKIM alignment).
Aggregate DMARC Reports:
An organization that published DMARC records will receive aggregate reports via mail from various domains as part of mail security. DMARC aggregate reports contain information about the authentication status of messages sent on behalf of a domain. With the reports, an organization can see which emails are authenticating against DKIM and SPF and which emails are rejected.
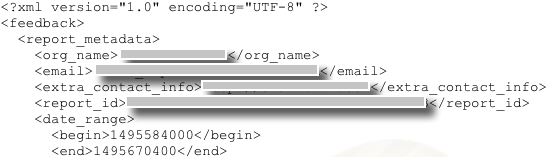
DMARC report mail contains reports in XML format. The below images shows the XML format structure and description.
The initial part of the report contains details like Reporting organization (organization sending reports) name, Reporting Organisation sending email address and additional contact information, data range in bytes and report id.
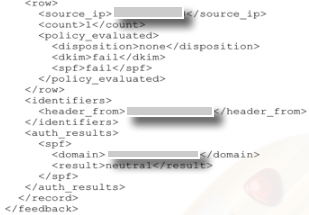
The next part of the report contains DMARC record information like from domain, dmarc policy status like reject or quarantine and per cent of mails subjected to policy.

The last part of the report describes the authentication summary with details like IP address in the mail, Disposition of the message, to show if the policy was applied, DKIM and SPF authentication results.
Why DMARC is Necessary:
When an organization requires mail services for business or transactional functions then DMARC is important for them to implement as this would prevent social engineering attacks like mail spoofing. Below are a few key reasons to implement DMARC in your organization,
- Publishing a DMARC record protects your brand by preventing unauthenticated parties from sending mail from your domain. This helps keep the reputation of an organization in the high end.
- DMARC record enables security for mails sent and received by organization employees, stakeholders etc.,
- configuring DMARC helps to receive mail servers determine how to evaluate messages that claim to be from your domain.
- The aggregate and Forensic reports sent by receiving mail servers will help to identify who sends mail from your domain.
DMARC Misconfiguration Threat:
The major threat to mail services due to lack of DMARC records or misconfiguration of DMARC records will be mail spoofing attacks. Email spoofing is part of social engineering technique where an attacker sends a mail to an organization’s employees or customers from one of the mail IDs of the same organization to carry out phishing or installing malware in their systems. The mails will be received in the user’s inbox due to a lack of DMARC record mail authentication.
In the below image we have checked the DMARC record of domain vulnweb.com (test domain) in an online tool.
Note: DMARC record can also be tested using DNS enumeration tools like dig in Linux as shown in the above sections.
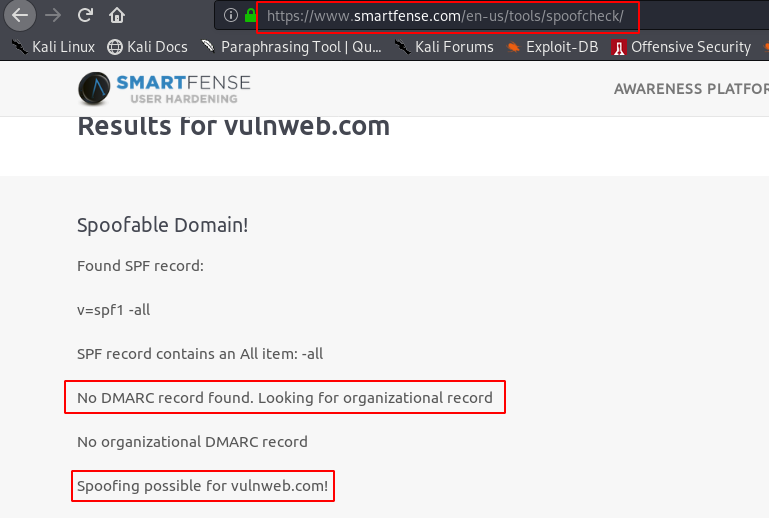
As we can see from the above screenshot, there is no DMARC record configured for this domain which leads to spoofing of legitimate mail id from this domain. We were able to spoof the vulnweb.com domain to send mail to some random user and found that the mail is in his inbox.
Conclusion:
DMARC records are an important evolution of email authentication. This is just an example of email senders and ISPs working together to protect the email channel. This blog lets the readers understand the need for DMARC records for their organization as it may lead to serious security threats if not configured properly.