We at Briskinfosec understand the gravity of the situation: Your most sensitive medical information isn't confined to a file cabinet in your local hospital. It's digitized, traveling across borders, and potentially accessible to entities you've never even heard of. In an age where a single data breach can expose millions, the security of patient information is no longer a local issue—it's a global imperative. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), while a US law, stands as a critical benchmark for protecting this data, and its influence is felt worldwide. We've seen firsthand how breaches erode trust and inflict lasting damage, and that's why we're so passionate about helping organizations get this right.
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) was enacted by the U.S. Congress in 1996 with the primary objective of establishing national standards for protecting sensitive patient health information and ensuring that individual’s medical records are handled securely across healthcare organizations, insurance providers, and business associates. Over the years, HIPAA regulations have evolved to address the increasing cybersecurity risks and technological advancements in the healthcare industry, reinforcing stringent data security measures to prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and identity theft.
Key Entities Covered by HIPAA
HIPAA compliance is mandatory for:
- Healthcare Providers - Hospitals, clinics, doctors, pharmacie
- Health Plans & Insurers - Insurance companies, HMOs
- Healthcare Clearinghouses - Entities processing health data
- Business Associates - IT vendors, cloud service providers, and third-party partners handling PHI
Did you know that the average cost of a healthcare data breach reached a staggering $10.93 million in 2023!
The Core Pillars of HIPAA Compliance
HIPAA is built on four key rules that define how patient data should be protected:
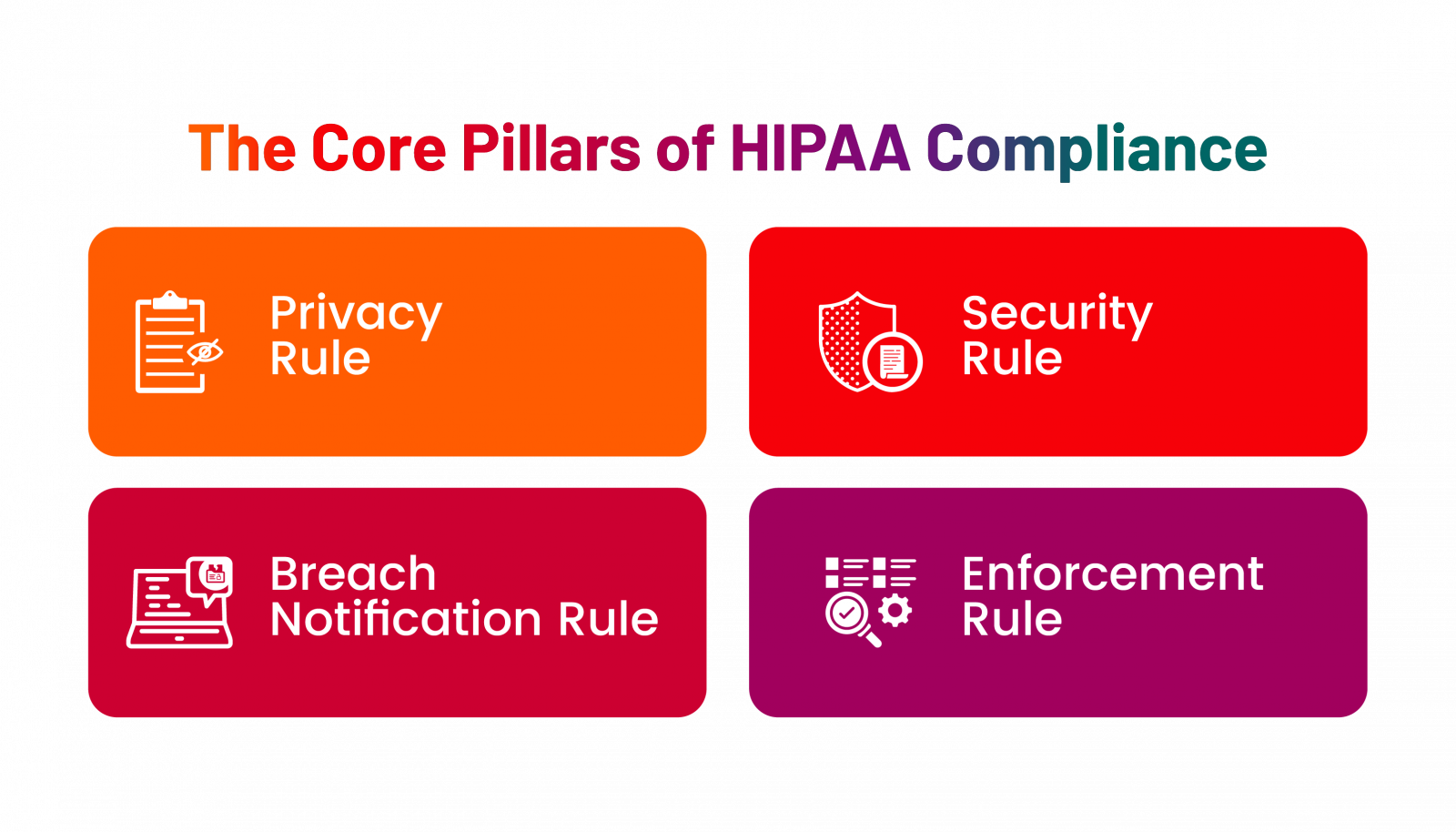
Privacy Rule: Protecting Patient Rights
- Only authorized individuals (doctors, nurses, insurance providers) can access patient data.
- Patients have the right to view, request, and control their medical records.
- Data cannot be shared without patient consent, except for specific legal or emergency scenarios.
A hospital cannot disclose a patient’s diagnosis to an employer without the patient’s explicit permission.
Security Rule: How is Patient Data Protected?
- Enforces encryption, access controls, and risk assessments for electronic PHI (ePHI).
- Requires ongoing security monitoring to detect potential breaches.
- Mandates disaster recovery plans to ensure business continuity after cyber incidents.
A healthcare provider must use encrypted emails when sending medical records to prevent unauthorized interception.
Breach Notification Rule: What Happens After a Data Breach?
If a healthcare organization suffers a data breach, it must:
- Requires immediate action after a data breach.
- Mandates notifications to affected patients and regulators within 60 days.
- Alert the media if the breach impacts more than 500 individuals.
Example: If a hospital’s database is hacked, it must promptly notify patients and regulators to mitigate potential damage.
Enforcement Rule – What Are the Consequences of Non-Compliance?
This rule defines penalties for HIPAA violations:
|
Violation Category |
Fine per Violation |
Annual Maximum Penalty |
|
Unintentional |
$100 - $50,000 |
$25,000 |
|
Reasonable Cause |
$1,000 - $50,000 |
$100,000 |
|
Wilful Neglect (Corrected) |
$10,000 - $50,000 |
$250,000 |
|
Wilful Neglect (Not Corrected) |
$50,000+ |
$1.5 million |
In severe cases, individuals responsible for violations may face criminal charges and up to 10 years in prison!
3 Key areas of HIPAA requirements
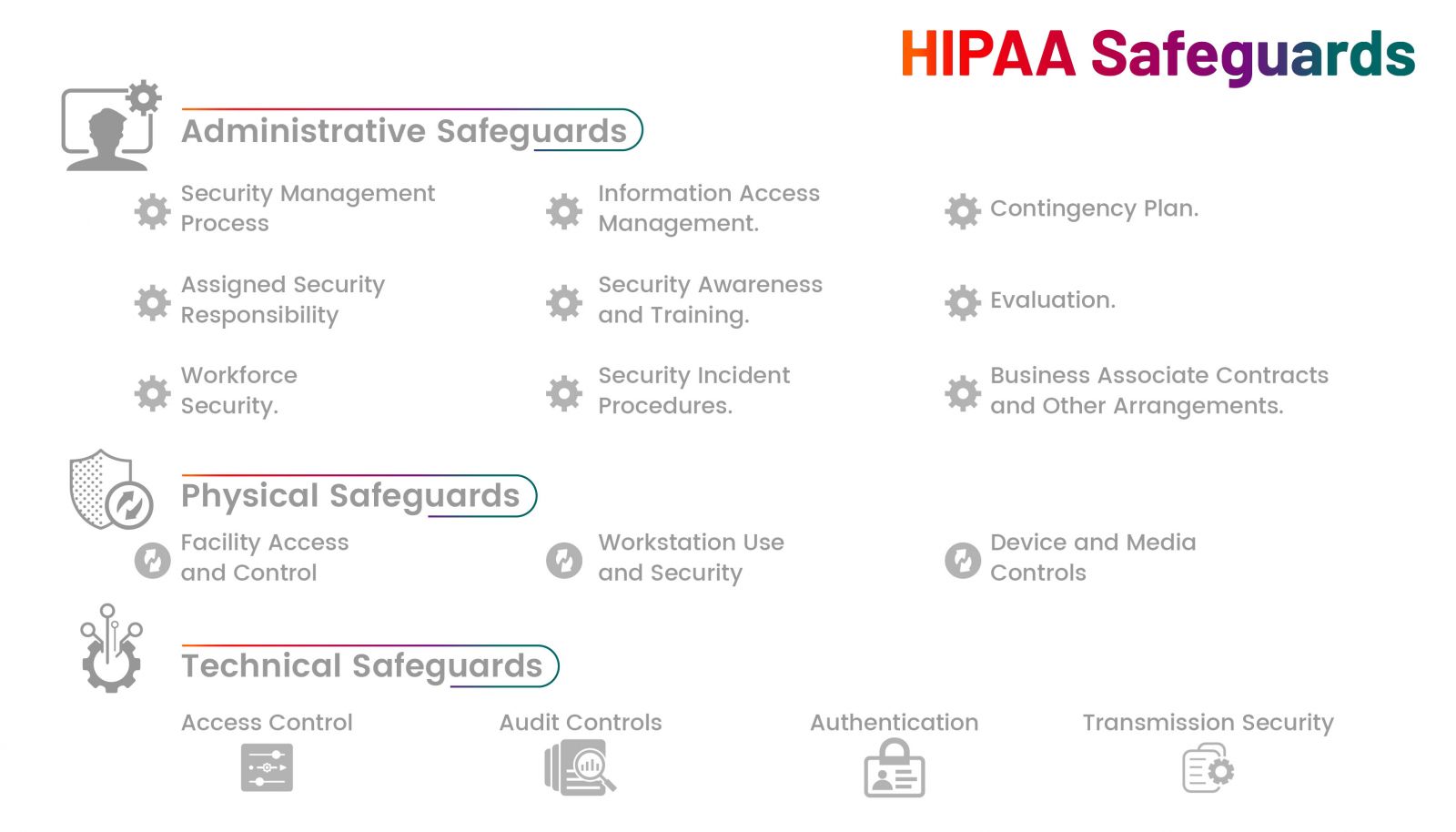
- Administrative Safeguards
These are the policies, procedures, and processes that govern how an organization manages the security of PHI. They focus on creating a strong security culture through strategic planning and proper workforce management.
Key Components:
- Security Management Process:Identifying potential risks to PHI and implementing measures to mitigate them. This includes regular risk assessments and audits.
- Workforce Training and Awareness: Ensuring that all employees understand HIPAA regulations, recognize phishing attempts, and handle patient data securely.
- Access Control Procedures: Implementing procedures to grant or restrict access to PHI based on an employee’s role and job responsibilities.
- Incident Response and Contingency Plans: Developing a strategy to detect, respond to, and recover from potential data breaches or security incidents.
- Business Associate Agreements (BAAs): Ensuring third-party vendors comply with HIPAA standards when accessing, processing, or transmitting PHI
- Physical Safeguards
Physical safeguards focus on protecting the hardware, systems, and physical locations where PHI is stored or accessed. This category addresses physical access control to prevent unauthorized individuals from accessing sensitive data.
Key Components:
- Facility Access Controls: Implementing controlled access to physical locations where PHI is stored, this can include restricted areas, key card access, and surveillance systems.
- Workstation and Device Security: Ensuring that computers, mobile devices, and other electronic systems accessing PHI are secure. This includes screen locks, data encryption, and policies for using portable devices.
- Hardware Disposal and Reuse: Proper disposal of outdated hardware, hard drives, or any device that stores PHI to prevent unauthorized data retrieval.
- Visitor Management: Monitoring and managing visitor access to areas where PHI is accessible, ensuring unauthorized individuals cannot view or access confidential information.
- Technical Safeguards
Technical safeguards are the technologies and policies used to protect and control access to PHI. These safeguards help maintain data integrity, confidentiality, and accessibility.
Key Components:
- Access Controls: Implementing user authentication mechanisms like passwords, biometric scans, and multi-factor authentication (MFA) to restrict unauthorized access.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting PHI both in transit and at rest to protect it from interception or unauthorized access.
- Audit Controls: Utilizing audit logs and monitoring tools to track access and activities involving PHI, helping to identify unauthorized access or breaches.
- Automatic Logoff: Ensuring that devices automatically log off after a period of inactivity to prevent unauthorized access.
- Integrity Controls: Implementing measures to prevent unauthorized alteration or destruction of PHI, ensuring its accuracy and reliability.
How Organizations Can Stay Ahead of Cyber Threats
Cyber threats won’t wait, and compliance alone is not enough. Organizations must adopt a proactive security mindset to reduce risks effectively. Here’s how:
- Implement Multi-Layered Security – Encryption, access controls, and endpoint security must work together.
- Train Employees Continuously – Human error remains one of the biggest threats to patient data security.
- Conduct Regular Risk Assessments – Identifying vulnerabilities before attackers do is key to preventing breaches.
- Strengthen Incident Response Plans – The faster an organization responds to a breach, the lower the damage.
Why Every Healthcare Domain Should Align with HIPAA Principles
Aligning with HIPAA, even outside the U.S., offers major advantages:
- Stronger Security – Reduces breach risks through tested safeguards
- Greater Trust – Builds patient confidence, crucial in global healthcare
- Legal Readiness – Supports compliance with other privacy laws
- Data Interoperability – Encourages secure cross-border data sharing
International Data Protection Laws
Many global laws mirror HIPAA’s intent to protect sensitive data:
- GDPR (EU) – Strict rules on consent, security, and breach response
- PIPL (China) – Regulates personal data collection and transfers
- NHS Act 2006 (UK) – Includes data confidentiality in public healthcare
- PHIPA (Canada) – Ontario’s law governing health data usage and sharing
Why HIPAA Compliance is More Important Than Ever
One of the most catastrophic healthcare data breaches in history occurred in 2015, when Anthem Inc., one of the largest health insurance providers in the United States, suffered a massive cyberattack that exposed 78.8 million patient records. The breach, which stemmed from a sophisticated phishing attack, allowed hackers to gain access to Anthem’s database containing highly sensitive patient data, including Social Security numbers, medical IDs, home addresses, employment details, and financial information.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
- HIPAA Violation: Anthem, Inc failed to implement proactive risk management strategies and lacked robust access controls, allowing cybercriminals to easily infiltrate their system.
- $16 Million Fine: The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) imposed a record-breaking HIPAA settlement fine, emphasizing the importance of strict cybersecurity practices in the healthcare sector.
- Severe Reputational Damage: Millions of affected individuals lost trust in Anthem’s ability to protect their private health information, leading to a drop in customer confidence and potential loss of business.
- Long-Term Legal Consequences: Anthem faced multiple class action lawsuits, further escalating financial losses and increasing the company’s legal liabilities.
How Briskinfosec Supports You in Safeguarding Patient Data
Achieving HIPAA compliance requires a comprehensive cybersecurity approach. As a healthcare business owner, you likely face significant challenges in navigating these complexities. That's where we come in.
At Briskinfosec, we bring over 8 years of experience as a reputed cybersecurity company, providing a holistic approach to HIPAA compliance. Our specialized services include:
- In-depth HIPAA Security Risk Assessments
- Vulnerability Assessments (VA) and Penetration Testing (PT)
- Incident Response Plans (IRP)
- Compliance-driven security monitoring
- Staff training, including HIPAA Security Awareness Training
- Third-Party Risk Management & Compliance Validation
Organizations that fail to secure patient data risk severe penalties, legal action, and reputational damage, and, more importantly, inflict serious harm on their patients. With our deep understanding of both HIPAA and cybersecurity, we're here to help you avoid those pitfalls and build a resilient security posture. We are among the top 30 HIPAA cybersecurity consulting firms, ready to assist you.
Let's Talk
We at Briskinfosec are confident that our 8 years of experience can help you navigate the complexities of HIPAA and build a robust security framework. We encourage you to book a meeting with us. Let's discuss your specific needs and how our expertise can protect your organization and your patients.


